5080 Michigan PDF Form
The Michigan Department of Treasury Form 5080, officially titled "2015 Sales, Use and Withholding Taxes Monthly/Quarterly Return," plays a crucial role for businesses operating within the state. This form enables businesses to report and remit sales taxes, use taxes, and withholding taxes, a requirement under the authority of Public Acts 167 of 1933 and 94 of 1937, as amended. It outlines specific instructions for accurately calculating the taxes due, taking into account gross sales, rentals, and services, including both in-state and out-of-state transactions. The form also details how to compute allowable discounts for timely filings, further breaking down the calculations based on the frequency of filing - monthly, quarterly, or as an accelerated filer. Additionally, it informs on the procedure for reporting use tax on items purchased for business or personal use, alongside the total amount of Michigan income tax withheld. With stipulations for calculating penalties and interest for late filings, the form facilitates compliance with Michigan tax laws, ensuring businesses contribute correctly to state revenues. However, it's essential to note that Form 5080 cannot be used for amended returns, directing taxpayers to the Amended Monthly/Quarterly Return (Form 5092) for such purposes.
Preview - 5080 Michigan Form
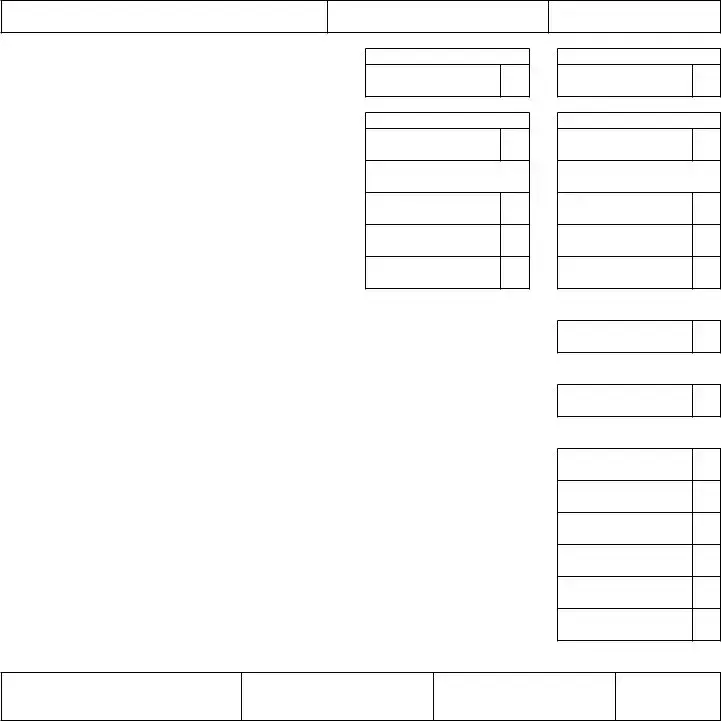
Michigan Department of Treasury 5080
2015 Sales, Use and Withholding Taxes Monthly/Quarterly Return
Issued under authority of Public Acts 167 of 1933 and 94 of 1937, as amended.
This form cannot be used as an amended return; see the Amended Monthly/Quarterly Return (Form 5092).
Taxpayer’s Business Name
Business Account Number (FEIN or TR Number)
Return Period Ending
PaRT 1: SaleS and USe Tax
1. Gross sales, rentals and services |
1a. |
Sales
1b.
Use: Sales and Rentals
2.Total sales and/or use tax. Multiply taxable sales,
rentals and services by 6% (0.06) .................................................
3.Total
4.Remaining amount of sales and use tax eligible for discount. Subtract line 3 from line 2..............................................................
5.Total of allowable discounts. Multiply line 4 by your applicable discount rate..................................................................................
2a.
3a.
4a.
5a.
a. Sales Tax
XXXXXXX
2b.
3b.
4b.
5b.
B. Use Tax
XXXXXXX
6. Total sales and use tax due. Subtract line 5 from line 4 |
6a. |
6b.
PaRT 2: USe Tax on ITeMS PURchaSed foR BUSIneSS oR PeRSonal USe
7. Total amount of use tax from purchases and withdrawals from inventory. |
|
Multiply taxable amount by 6% (0.06) |
7. |
PaRT 3: WIThholdIng Tax
8. Total amount of Michigan income tax withheld |
8. |
PaRT 4: ToTal Tax/PayMenT dUe
9. |
Amount of sales, use and withholding tax due. Add lines 6a, 6b, 7, and 8. If amount is negative, this is the |
|
|
amount available for future tax periods (skip lines |
9. |
10. |
Overpayment from prior return period or amount previously paid for this return period |
10. |
11. |
Amount of tax due. Subtract line 10 from line 9 |
11. |
12. |
Penalty paid with this return (for late iling) |
12. |
13. |
Interest paid with this return (for late iling) |
13. |
14. |
PayMenT dUe. Add lines 11, 12 and 13 |
14. |
Taxpayer Certiication. I declare under penalty of perjury that this return is true and complete to the best of my knowledge.
Signature of Taxpayer or Oficial Representative (must be Owner, Oficer, Member, Manager, or Partner)
Printed Name
Title
Date
Make check payable to “State of Michigan” and include your account number on your check.
Send your return and any payment due to: Michigan Department of Treasury, P.O. Box 30324, Lansing, MI
+ 0000 2015 66 01 27 1

Instructions for 2015 Sales, Use and Withholding Taxes Monthly/Quarterly Return (Form 5080)
IMPORTANT: This is a return for Sales Tax, Use Tax, and/ or Withholding Tax. If the taxpayer inserts a zero on (or leaves blank) any line for reporting Sales Tax, Use Tax, or Withholding Tax, the taxpayer is certifying that no tax is owed for that tax type. If it is determined that tax is owed, the taxpayer will be liable for the deficiency as well as penalty and interest.
PaRT 1: SaleS and USe Tax
Line 1a: Total gross sales for tax period being reported. Enter the total of your Michigan sales of tangible personal property including cash, credit and installment transactions and any costs incurred before ownership of the property is transferred to the buyer (including shipping, handling, and delivery charges).
Line 1b: This line is used to report the following:
•
•Lessors of tangible personal property: Enter amount of total rental receipts.
•Persons providing accommodations: This would include but not limited to hotel, motel, and vacation home rentals. This also includes assessments imposed under the Convention and Tourism Act, the Convention Facility Development Act, the Regional Tourism Marketing Act, the Community Convention or Tourism Marketing Act.
•Telecommunications Services: Enter gross income from telecommunications services.
Line 2a: Total sales tax. Negative figures are not allowed or valid.
Line 2b: Total use tax. Negative figures not allowed or valid.
Line 5: Enter total allowable discounts. Discounts apply only to 2/3 (0.6667) of the sales and/or use tax collected at the 6 percent tax rate. See below to calculate your discount based on filing frequency:
Monthly Filer
•If the tax is less than $9, calculate the discount by multiplying the tax by 2/3 (.6667).
•Enter $6 if tax is $9 to $1,200 and paid by the 12th, or $9 to $1,800 and paid by the 20th .
•If the tax is more than $1,200 and paid by the 12th,
calculate discount using this formula: (Tax x .6667 x .0075). The maximum discount is $20,000 for the tax period.
•If the tax is more than $1,800 and paid by the 20th,
calculate discount using this formula: (Tax x .6667 x .005). The maximum discount is $15,000 for the tax period.
Quarterly Filer
•If the tax is less than $27, calculate the discount by multiplying the tax by 2/3 (.6667)
•Enter $18 if tax is $27 to $3,600 and paid by the 12th, or $27 to $5,400 and paid by the 20th.
•If the tax is more than $3,600 and paid by the 12th,
calculate discount using this formula: (Tax x .6667 x .0075). The maximum discount is $20,000 for the tax period.
•If the tax is more than $5,400 and paid by the 20th,
calculate discount using this formula: (Tax x .6667 x .005). The maximum discount is $15,000 for the tax period.
Accelerated Filer
•If the tax is paid by the 20th, calculate discount using this formula: (Tax x .6667 x .005). No maximum discount applies.
PaRT 2: USe Tax on ITeMS PURchaSed foR BUSIneSS oR PeRSonal USe
Line 7: To determine your use tax due from purchases and withdrawals, multiply the total amount of your inventory value by 6% (0.06) and enter here.
PaRT 3: WIThholdIng Tax
Line 8: Enter the total Michigan income tax withheld for the tax period.
PaRT 4: ToTal Tax/PayMenT dUe
Line 9: If amount is negative, this is the amount available for
future tax periods (skip lines
Line 10: Enter any payments you submitted for this period, prior to filing the return. If you are using an overpayment from a previous period only enter the amount needed to pay the total liability for this return. In the event an overpayment still exists declare it on the next return you file with a liability. (Liability minus overpayments/prior payment for this period must be greater than or equal to zero).
How to Compute Penalty and Interest
If your return is filed with additional tax due, include penalty and interest with your payment. Penalty is 5% of the tax due and increases by an additional 5% per month or fraction thereof, after the second month, to a maximum of 25%. Interest is charged daily using the average prime rate, plus 1 percent.
Refer to www.michigan.gov/taxes for current interest rate information or help in calculating late payment fees.
Form Characteristics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Governing Laws | Issued under the authority of Public Acts 167 of 1933 and 94 of 1937, as amended. |
| Form Purpose | 2015 Sales, Use, and Withholding Taxes Monthly/Quarterly Return. |
| Non-Amendable | This form cannot be used for amended returns; Form 5092 must be used instead. |
| Sales and Use Tax Calculation | Taxable sales, rentals, and services are multiplied by 6% (0.06). |
| Pre-paid Tax Credits | Includes pre-paid tax from Form 5083, 5085, or 5086 (e-file only). |
| Allowable Discounts | Discounts are applicable only to 2/3 (0.6667) of the sales and/or use tax collected at the 6 percent rate. |
| Use Tax on Purchases | For business or personal use items, multiply the inventory value by 6% (0.06). |
| Withholding Tax Reporting | Enter the total Michigan income tax withheld for the tax period. |
| Total Tax/Payment Due Calculation | Adds up total sales, use, and withholding taxes due. Negative amounts carry over for future periods. |
| Penalty and Interest for Late Filing | Penalty starts at 5% of the tax due, increasing by 5% per month after the second month, maxing out at 25%. Interest is the prime rate plus 1%, charged daily. |
Guidelines on Utilizing 5080 Michigan
Filing the Michigan Department of Treasury 5080 form is a significant step for taxpayers in Michigan to comply with state tax obligations pertaining to sales, use, and withholding taxes. This form, crucial for both monthly and quarterly filers, helps ensure that businesses accurately report and remit taxes due to the state. Careful attention to detail and adherence to the instructions for filling out each section will facilitate a smoother process. Following are step-by-step instructions designed to help taxpayers accurately complete and submit the form.
- Start by providing the Taxpayer’s Business Name and the Business Account Number. The Business Account Number can be either your Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or your Treasury Registration (TR) Number.
- Next, enter the Return Period Ending date in the format MM-YYYY to indicate the specific period for which you are filing.
- In Part 1: Sales and Use Tax, record the total gross sales, rentals, and services under section 1, broken down into:
- 1a. Sales: Total Michigan sales of tangible personal property.
- 1b. Use: Sales and Rentals from out-of-state retailers, lessors, or services including accommodations and telecommunications.
- Calculate the Total sales and/or use tax by multiplying taxable sales, rentals, and services by 6% (line 2).
- Enter the Total pre-paid tax from Form 5083, 5085, or 5086 under section 3, if applicable.
- Determine the Remaining amount of sales and use tax eligible for discount (line 4) by subtracting line 3 from line 2.
- Compute the Total of allowable discounts (line 5) using your applicable discount rate based on your filing frequency (monthly, quarterly, or accelerated filer).
- Under Part 2: Use Tax on Items Purchased for Business or Personal Use, calculate the total amount of use tax from purchases and withdrawals by multiplying the taxable amount by 6% and enter this in line 7.
- In Part 3: Withholding Tax, enter the Total amount of Michigan income tax withheld for the tax period on line 8.
- For Part 4: Total Tax/Payment Due, add the amounts from lines 6a, 6b, 7, and 8 to determine the total amount due (line 9).
- If there's an Overpayment from prior return period or amount previously paid for this period, enter this amount on line 10.
- Calculate the Amount of tax due by subtracting line 10 from line 9 and enter this on line 11.
- Include any Penalty paid with this return (for late filing) on line 12 and any Interest paid with this return (for late filing) on line 13.
- The Payment Due (line 14) is calculated by adding lines 11, 12, and 13. This is the final amount you owe.
- Complete the Taxpayer Certification section at the end of the form by signing and providing the printed name, title, and date to declare under penalty of perjury that the return is accurate.
- Finally, make your check payable to “State of Michigan” and include your account number on the check. Mail your completed return and any payment due to the address provided: Michigan Department of Treasury, P.O. Box 30324, Lansing, MI 48909-7824.
Tackling tax forms can be daunting, but by breaking down the process into manageable steps, taxpayers can fulfill their obligations efficiently and accurately. Always ensure to double-check calculations and information to prevent errors. Remember, it's essential to meet the filing and payment deadlines to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Crucial Points on This Form
What is the purpose of the Michigan Form 5080?
Michigan Form 5080 is designed for reporting and paying sales, use, and withholding taxes on a monthly or quarterly basis. The form is issued under the authority of Public Acts 167 of 1933 and 94 of 1937, as amended. Sales tax is applied to the sale of tangible personal property and certain services, use tax is for tangible personal property and services used in Michigan but purchased out of state or online, and withholding taxes are for income withheld from employees' wages.
Who needs to file Michigan Form 5080?
Businesses operating within Michigan must file Form 5080 if they collect sales tax, use tangible personal property or services for which use tax is due, or if they have employees and withhold Michigan income tax from their wages. This includes out-of-state retailers with no physical presence in Michigan but who have sales and transactions in the state, lessors of tangible personal property, and providers of accommodations, among others.
How can discounts be calculated on Form 5080?
Discounts on Form 5080 depend on the filing frequency and the amount of sales and/or use tax collected. Discounts apply only to 2/3 of the tax collected at the 6 percent rate. For monthly filers, different calculation methods are used depending on the total tax collected, with specific formulas and maximum discount limits provided for taxes collected up to, and in excess of, certain amounts. Quarterly filers have similar calculations with their own set criteria and maximum discounts. Accelerated filers calculate discounts using a specific formula, with no maximum limit on the discount available.
What should be done if there's a mistake on a filed Form 5080?
If a mistake is discovered on a previously filed Form 5080, the taxpayer should not use another Form 5080 to correct it. Instead, the Amended Monthly/Quarterly Return (Form 5092) must be used to make any corrections to previously filed forms. This ensures that the Michigan Department of Treasury accurately tracks and records the amendment to your tax liabilities.
What are the penalties and interest for late filing or payment of the taxes due on Form 5080?
If the return or payment is late, penalties and interest will apply. Penalties are computed as 5% of the unpaid tax due, which increases by an additional 5% per month or fraction thereof, after the second month, up to a maximum of 25%. Interest accumulates daily at a rate of the average prime rate plus 1 percent. For the most current rates and help in calculating any penalties and interest that may be due, taxpayers are advised to visit the Michigan Department of Treasury's official website.
Common mistakes
When filling out the 5080 Michigan form, a common mistake is inaccurately reporting gross sales, rentals, and services in Part 1, lines 1a and 1b. It's crucial to include all Michigan sales of tangible personal property, including cash, credit, and installment transactions, as well as any pre-sale costs such as shipping, handling, and delivery charges. Failure to correctly report these amounts can lead to discrepancies in tax liabilities and could attract penalties for underreporting.
Another error occurs in the calculation of total sales and/or use tax (line 2). Taxpayers must multiply taxable sales, rentals, and services by 6% (0.06). An incorrect application of this rate, either from mathematical errors or misunderstanding of what constitutes taxable sales, can significantly affect the total tax due. Ensuring accuracy in this step is essential for compliance and to prevent potential fines.
Incorrectly applying discounts in line 5 is also a frequent oversight. Discounts are only applicable to two-thirds (0.6667) of the sales and/or use tax collected at the 6 percent rate. The structure of these discounts varies depending on the filing frequency—monthly, quarterly, or as an accelerated filer. Misunderstanding the calculation or eligibility can result in declaring a higher or lower discount than allowed, affecting the total sales and use tax due.
Lastly, misunderstanding or neglecting Part 2, which deals with use tax on items purchased for business or personal use, leads to errors. Line 7 requires taxpayers to multiply the total value of their taxable inventory purchases by 6% (0.06). Some individuals mistakenly leave this section blank or incorrectly calculate their tax due, not realizing that all tangible personal property bought for use, storage, or consumption within Michigan that hasn't been taxed by another state falls under this category. Accurate completion of this section is crucial for total tax compliance.
Documents used along the form
When managing taxes in Michigan, especially for businesses involved in sales, use, and withholding tax activities, it is essential to become familiar with numerous forms and documents beyond the 5080 Michigan form. These documents are integral for a broad spectrum of tax-related responsibilities, from reporting additional earnings to correcting previously filed returns. Here's a concise guide to other vital forms and documents often used in conjunction with Form 5080.
- Form 5092: This form serves as the Amended Monthly/Quarterly Return. It's used when corrections need to be made to previously submitted Form 5080 information. This is crucial for ensuring accurate tax reporting and compliance.
- Form 5083: Prepaid Sales Tax Return for Fuel. This form is used by fuel sellers to report and remit prepaid sales tax on fuel purchases. It ties into Form 5080 by accounting for pre-paid taxes that may affect sales and use tax liabilities.
- Form 5085: Prepaid Sales Tax Return for Gasoline and Diesel Fuel. Similar to Form 5083, this document is essential for businesses dealing with gasoline and diesel fuel, enabling them to report prepaid sales tax specific to these fuels.
- Form 5086: Prepaid Wireless Sales Tax Return. Retailers of prepaid wireless telecommunications services use this form to report and remit sales tax collected on the sale of prepaid wireless services and products.
- UIA 1028: Employer's Quarterly Wage/Tax Report. Employers must submit this form to report wages paid, taxable wage base, and unemployment tax due for each quarter.
- Form 165: Annual Return for Michigan Taxes. This comprehensive form is used by businesses to report their annual sales, use, and withholding taxes in a consolidated manner.
- Form 160: Combined Return for Michigan Taxes. Similar to Form 165 but designed for more frequent filing, this form allows for the combined reporting of various Michigan taxes on a monthly or quarterly basis.
- Form 3372: Michigan Sales and Use Tax Certificate of Exemption. Businesses use this document to claim exemption from Michigan sales and use tax on qualified transactions, affecting the reporting on Form 5080.
- MI-W4: Employee's Michigan Withholding Exemption Certificate. Employers require this form from employees to determine the correct amount of state income tax to withhold, influencing the withholding tax part of Form 5080.
- Form 5278: Application for Deferment of Summer Taxes. This form allows property owners to apply for a deferment of summer property taxes, which might indirectly impact business financials and tax liabilities reported on Form 5080.
Understanding and effectively managing the forms that complement Form 5080 can significantly streamline a business’s tax processes in Michigan. Each document plays a distinct role in ensuring that businesses accurately report and comply with the state’s various tax obligations. Familiarity with these forms not only aids in maintaining good standing with tax authorities but also optimizes financial management and planning.
Similar forms
Several documents are similar to the 5080 Michigan Form, which is a comprehensive return used for reporting Sales Tax, Use Tax, and Withholding Tax. These documents also serve for tax reporting purposes but may differ in terms of their specific uses, jurisdictions, or the types of taxes they address. Let's explore ten such documents:
- Form 1040 (U.S. Individual Income Tax Return): Similar to the 5080 form, the 1040 Form is used by individuals to file their annual income taxes with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Both require detailed income and tax payment information, although the 1040 Form focuses on personal income taxes at the federal level.
- Schedule C (Profit or Loss from Business): This form accompanies Form 1040 for those reporting income or loss from a business they operated or a profession they practiced as a sole proprietor. Like the 5080, it deals with income but focuses on business operations specifically.
- Form 941 (Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return): Similar to the withholding section of the 5080 form, Form 941 is used by employers to report income taxes, Social Security tax, or Medicare tax withheld from employees' paychecks. It also reports the employer's portion of Social Security or Medicare tax.
- Form W-2 (Wage and Tax Statement): This form is issued by employers to employees and the IRS, showing the employee's annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck, paralleling the withholding tax reporting aspect of the 5080, but from an employee-specific viewpoint.
- Form 1099 (Various): The 1099 forms are used to report various types of income other than salaries, wages, and tips (like Form W-2). Similar to the 5080 form, it's used for tax reporting but focuses on miscellaneous income.
- Form W-4 (Employee’s Withholding Certificate): While the 5080 includes calculations for withheld taxes, Form W-4 is filled out by employees to inform employers of how much tax to withhold from their paycheck, impacting the accuracy of withholdings reported on the 5080.
- Form W-9 (Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification): This form is used to provide the correct taxpayer identification number (TIN) to the person who is required to file an information return with the IRS. It's similar to the 5080 as part of tax reporting documentation, ensuring accurate taxpayer identification.
- Form 1120 (U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return): Similar to the 5080, Form 1120 is used by corporate entities to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, and to calculate their income tax liability. It focuses on corporate rather than sales, use, and withholding taxes.
- Form 5083 (Prepaid Sales Tax on Fuel): Specifically mentioned in the 5080 instructions, Form 5083 is used for reporting and paying prepaid sales tax on fuel, showcasing a specific tax type that contributes to the total tax reporting similar to the sales tax section of the 5080.
- Form 5092 (Amended Monthly/Quarterly Return): Directly related to the 5080 form, Form 5092 is for amending previously filed 5080 forms. It illustrates the process for correcting or updating information on the original sales, use, and withholding tax returns filed with the Michigan Department of Treasury.
Each of these documents, while serving distinct purposes or focusing on different tax elements, shares the common objective of facilitating tax reporting and compliance, akin to the functionalities provided by the 5080 Michigan form.
Dos and Don'ts
Filing the Michigan 5080 form, which is utilized for monthly/quarterly sales, use, and withholding taxes, requires careful attention to detail. To ensure accuracy and avoid common pitfalls, here are several do's and don'ts.
Do:- Double-check the business account number. This number is crucial for linking your return to the correct account. A mistake here can result in processing delays.
- Accurately report all gross sales, rentals, and services. Include every transaction to ensure your tax calculation is precise.
- Calculate discounts correctly based on your filing frequency. Understanding how to properly apply your allowable discounts can reduce the amount of tax owed.
- Enter the total Michigan income tax withheld. This figure should match your payroll records for the period.
- Sign and date the return. An unsigned return is not valid and can lead to unnecessary complications.
- Leave any sections blank if they apply to your business operations. Zeroes certify that no tax is owed for that section; incorrect certifications can lead to penalties and interest charges.
- Use the form as an amended return. If you need to correct a mistake, you must use Form 5092, the Amended Monthly/Quarterly Return.
- Ignore the deadline for submission. Late filing can result in penalties and interest charges, adding to the total amount owed.
- Misplace the completed form. Always keep a copy for your records before sending the original to the Michigan Department of Treasury.
- Forget to include payment if due. Make the check payable to the "State of Michigan" and note your account number on the check to ensure it’s credited properly.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can complete the Michigan 5080 form more accurately and efficiently, helping to ensure that your business remains compliant with state tax laws.
Misconceptions
When it comes to the 5080 Michigan form, several misunderstandings can lead to confusion. Here is a rundown of seven common misconceptions and the realities behind them.
- It's only for large businesses: The 5080 form is not exclusive to large businesses. Small and medium businesses, including sole proprietors who collect sales, use, or withholding tax, are also required to file it.
- It's an annual return: The 5080 form can be confusing because it's actually for monthly or quarterly reporting, not an annual return. The frequency of your filing depends on the volume of your transactions and the specific tax type.
- Amendments are filed on the same form: If you need to amend your 5080 form, you shouldn't do it on a fresh 5080 form. Amendments require the Amended Monthly/Quarterly Return (Form 5092). This is a common mistake that can lead to processing delays.
- Discounts don't apply to all: Not every filer is eligible for discounts on their tax liabilities. Discounts are calculated based on the timing of your payment and the total amount, with specific caps for monthly, quarterly, and accelerated filers.
- Negative figures are allowed: When reporting taxes owed on the 5080, negative figures are not permitted. This is a common error that can result in an incorrect calculation of taxes owed.
- Use tax is only for large purchases: This misunderstanding could lead to compliance issues. The use tax portion of the form is required for any business purchase where sales tax wasn't collected at the point of sale, regardless of the purchase size.
- All businesses must file it electronically: While electronic filing is strongly encouraged for efficiency and environmental reasons, businesses have the option to file their 5080 form by mail. However, specific forms related to payments, like the 5083, 5085, and 5086, are electronic-only.
Understanding these misconceptions about the Michigan 5080 form can help ensure accurate and timely filing, avoid penalties, and take advantage of any applicable discounts or benefits. Always refer to the latest instructions from the Michigan Department of Treasury to guide your tax reporting and payment efforts.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the 5080 Michigan form correctly is crucial for businesses in Michigan to ensure compliance with state tax regulations. Here are some key takeaways to remember:
- Understand the sections: The form is divided into multiple sections - Sales and Use Tax, Use Tax on Items Purchased for Business or Personal Use, Withholding Tax, and Total Tax/Payment Due. Each section requires different information related to business transactions.
- Reporting sales and use tax: In the Sales and Use Tax part, gross sales, rentals, and services are reported alongside the taxable amount subject to a 6% tax rate. It's key to differentiate between sales tax and use tax, as they apply to different types of transactions.
- Calculating discounts: Discounts on taxes due are available based on timely payment and the amount of tax. The discount calculation varies for monthly, quarterly, and accelerated filers, with specific formulas and caps for each category.
- Use tax on purchases: For items purchased for business or personal use that have not been taxed, use tax must be calculated at a 6% rate and reported in the relevant section of the form.
- Penalties and interest: Late filings are subject to penalties and interest. The form outlines how to calculate these additional charges, with the penalty starting at 5% of the tax due and increasing over time, and interest calculated using the prime rate plus 1%.
It's essential for businesses to pay close attention to each part of the form, ensuring accurate reporting of sales, use, and withholding taxes to avoid potential penalties and interest for late or incorrect filings. Additionally, understanding the available discounts for timely payments can provide financial benefits to filers.
Popular PDF Templates
2023 Michigan Tax Forms - Provides a structured format for companies to report and pay taxes on motor fuel imports or diversions within a three-day window.
Mi-1040 Form 2023 - Form 2248 transforms how businesses in Michigan manage tax payments, enabling a transition to electronic funds transfers.